In today’s fast-paced digital world, enterprise technology has become a cornerstone for businesses aiming to stay competitive. Enterprise technology encompasses a broad range of digital tools and systems designed to streamline business processes, enhance productivity, and drive innovation. This comprehensive guide will delve into the core components of enterprise technology, its role in the modern business landscape, emerging trends, challenges in implementation, and key considerations for organizations looking to leverage these technologies effectively.
Two Core Components of Enterprise Technology
At the heart of enterprise technology lie several key systems that are crucial for efficient operations and strategic management. These core components include ERP systems, CRM software, and SCM systems.
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning)
ERP systems are integrated platforms that help organizations manage and automate various business processes. By consolidating data from different departments into a single system, ERP facilitates seamless information flow across the organization, enhancing efficiency and decision-making.
- Functionality: ERP covers areas such as finance, HR, supply chain, and manufacturing.
- Benefits: Improved productivity, better resource management, and real-time data insights.
- Challenges: High implementation costs and complex integration with existing systems.
CRM (Customer Relationship Management)
CRM software is designed to manage a company’s interactions with current and potential customers. It helps businesses nurture customer relationships, improve customer service, and drive sales growth.
- Functionality: CRM encompasses customer data management, sales automation, and customer support.
- Benefits: Enhanced customer satisfaction, increased sales, and improved customer loyalty.
- Challenges: Ensuring data accuracy and user adoption across the organization.
SCM (Supply Chain Management)
SCM systems optimize the flow of goods, information, and finances involved in the production and delivery of products. These systems aim to reduce costs, enhance efficiency, and ensure timely delivery.
- Functionality: SCM includes procurement, production planning, inventory management, and logistics.
- Benefits: Reduced operational costs, improved supplier relationships, and enhanced production efficiency.
- Challenges: Managing supply chain disruptions and integrating with global suppliers.
Enterprise Technology in the Modern Business Landscape
In the contemporary business environment, enterprise technology plays a pivotal role in driving operational efficiency and strategic growth. Here’s how it impacts various aspects of business:
Streamlined Operations
Enterprise software solutions like ERP and SCM automate and integrate business processes, leading to streamlined operations and reduced manual intervention. This automation enhances productivity and ensures consistency across the organization.
- Example: A manufacturing company implementing ERP can automate its production scheduling and inventory management, reducing delays and optimizing resource use.
Data-Driven Decision-Making
Modern enterprise technology enables data-driven decision-making by providing real-time insights and analytics. Organizations can leverage big data and business intelligence tools to make informed decisions and predict future trends.
- Example: Retailers using CRM software can analyze customer purchase patterns to personalize marketing campaigns and improve customer engagement.
Enhanced Collaboration
Enhanced collaboration tools, facilitated by enterprise technology, break down silos and promote cross-functional teamwork. Cloud-based platforms and communication tools enable employees to collaborate efficiently, irrespective of their geographical locations.
- Example: A global company using cloud computing can have teams from different regions work together on projects in real-time, improving productivity and innovation.
Emerging Trends in Enterprise Technology
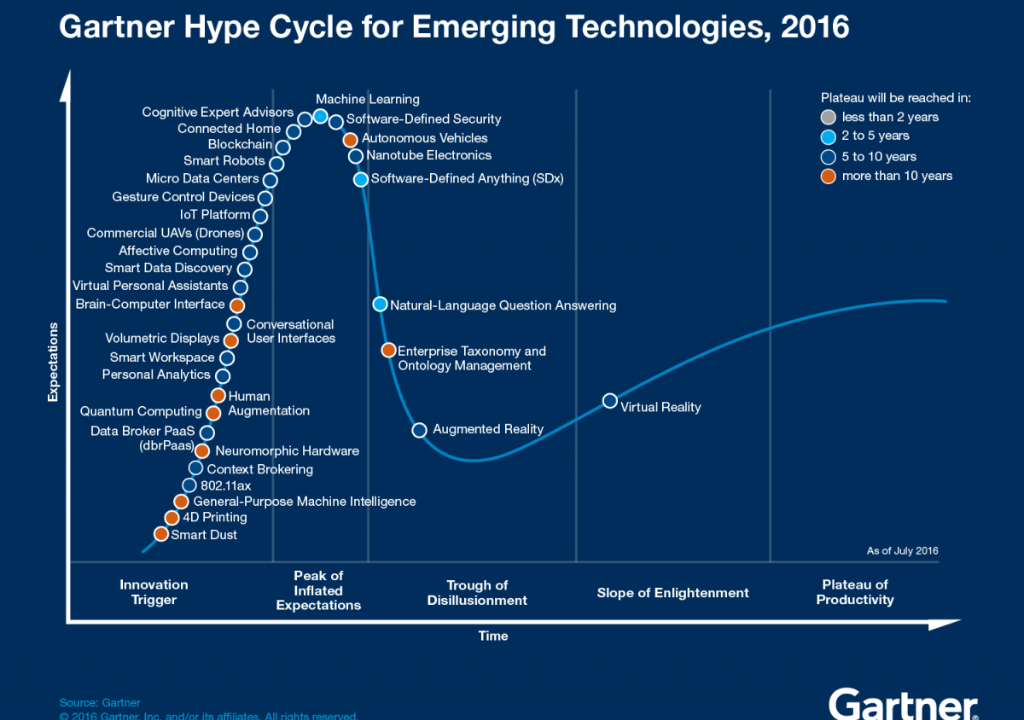
As we look forward to 2024, several emerging trends are shaping the future of enterprise technology. These trends are poised to transform how businesses operate and compete in the market.
AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are revolutionizing enterprise technology by automating complex tasks, enhancing predictive analytics, and personalizing customer experiences. These technologies enable businesses to process vast amounts of data and derive actionable insights.
- Example: Financial institutions using AI to detect fraudulent transactions and enhance cybersecurity measures.
Cloud Computing and SaaS
Cloud computing and Software as a Service (SaaS) models are becoming integral to enterprise technology. They offer scalable and cost-effective solutions, allowing businesses to access and deploy software over the internet without extensive on-premises infrastructure.
- Example: Startups leveraging cloud-based ERP systems to scale operations without significant upfront investment.
Cybersecurity in Enterprise Technology
With the increasing reliance on digital tools, cybersecurity has become a critical concern for businesses. Protecting sensitive data and ensuring compliance with regulations are paramount in the modern digital landscape.
- Example: Companies adopting advanced cybersecurity measures like multi-factor authentication and encryption to safeguard their data from cyber threats.
The Challenges (and Solutions) in Implementing Enterprise Technology
Implementing enterprise technology comes with its set of challenges. Understanding these obstacles and finding effective solutions is crucial for successful technology adoption.
Common Obstacles in Adopting Enterprise Technology
Organizations often encounter several common obstacles when adopting enterprise technology. These can include high costs, complex integration processes, and ensuring user adoption.
- Example: A mid-sized business struggling to justify the ROI on implementing an ERP system due to high initial costs.
Resistance to Change
Resistance to change is a significant hurdle in the implementation of enterprise technology. Employees may be hesitant to adopt new systems and processes, fearing disruption and a steep learning curve.
- Solution: Providing comprehensive training and involving employees in the implementation process can mitigate resistance and ensure smoother transitions.
Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating new enterprise technology with existing systems can be complex and time-consuming. Ensuring compatibility and seamless data flow between different systems is essential for effective implementation.
- Solution: Partnering with experienced IT professionals and using middleware solutions can facilitate smoother integrations.
Enterprise Technology
Understanding the intricacies of enterprise technology can help organizations avoid common pitfalls and achieve successful digital transformation. Here are some critical insights into the world of enterprise technology.
13 Reasons for Digital Transformation Failures and Real-World Examples
Despite the potential benefits, many digital transformation projects fail. Common reasons include lack of clear strategy, inadequate change management, and underestimating the complexity of technology integration.
- Real-World Example: A large retailer’s failed attempt to implement a new CRM system due to insufficient training and resistance from the sales team.
What Is Employee Separation? Definition, Types & Process
Employee separation is a critical HR process involving the termination of the employment relationship between an employee and an organization. Understanding its types (voluntary and involuntary) and ensuring a smooth process is vital for maintaining workplace harmony.
- Importance: Proper employee separation processes ensure legal compliance and protect the company’s reputation.
What Is Talent Management and Why Is It Important for HR?
Talent management involves attracting, developing, and retaining skilled employees to meet organizational goals. It is crucial for HR to ensure the company has the right talent in place to drive growth and innovation.
- Importance: Effective talent management leads to higher employee engagement, better performance, and reduced turnover rates.
What Is Employee Separation?
In conclusion, enterprise technology is a dynamic and essential component of modern business operations. By leveraging systems like ERP, CRM, and SCM, companies can streamline processes, make data-driven decisions, and enhance collaboration. Keeping abreast of emerging trends such as AI, cloud computing, and cybersecurity is crucial for staying competitive. While challenges exist in implementing these technologies, understanding and addressing these issues can lead to successful digital transformation and sustained business growth. As we move into 2024, the strategic use of enterprise technology will continue to be a key differentiator for leading organizations.
Conclusion
Enterprise technology is a vital component of modern business infrastructure, providing the tools and systems necessary to streamline operations, enhance decision-making, and foster collaboration across large organizations. By integrating critical functions through ERP systems, CRM software, and SCM solutions, businesses can achieve greater efficiency, improve customer relations, and optimize supply chain management. As trends such as AI, cloud computing, and cybersecurity continue to evolve, enterprise technology remains at the forefront of driving innovation and maintaining competitive advantage.
FAQ’ s
What is the meaning of enterprise information technology?
Enterprise information technology refers to the comprehensive set of digital tools, systems, and infrastructure that organizations use to manage and support large-scale business operations.
What is an example of an enterprise?
An example of an enterprise is a multinational corporation like Microsoft. Microsoft operates on a global scale, employing thousands of employees, and offers a wide range of products and services in various markets.
What is an example of an enterprise product?
An example of an enterprise product is SAP’s ERP software. This software helps large organizations manage business processes by integrating various functions such as finance, human resources, procurement, and supply chain management into a unified system.
What is IT called enterprise?
IT is called “enterprise” when it is designed to cater to the needs of large organizations rather than individual consumers or small businesses. Enterprise IT solutions are typically scalable, robust, and capable of handling complex processes and large volumes of data.
What is the definition of an enterprise?
An enterprise is a large organization or business entity engaged in commercial, industrial, or professional activities. It is characterized by its structured operations, multiple departments or units, and the scale at which it operates, often involving complex management and coordination of resources.
